Understanding the Hearing Test Process
If you’ve scheduled a hearing test for the first time in a few years,
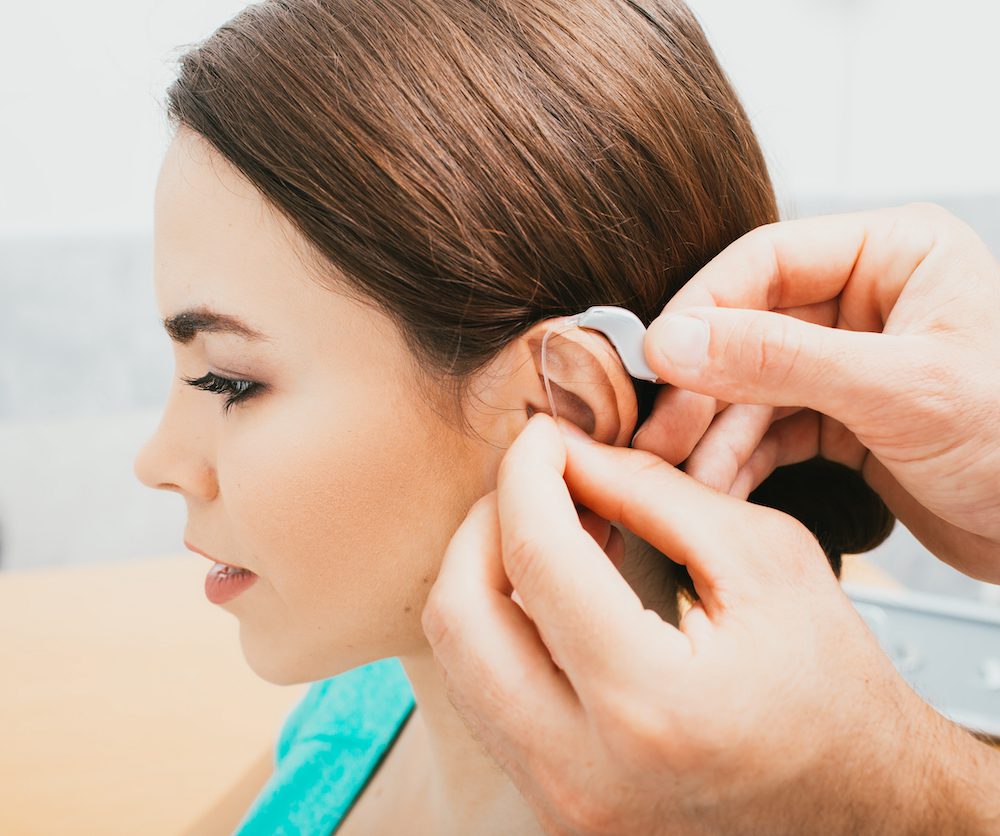

If you’ve scheduled a hearing test for the first time in a few years,

When it comes to hearing protection, prevention will always be better than
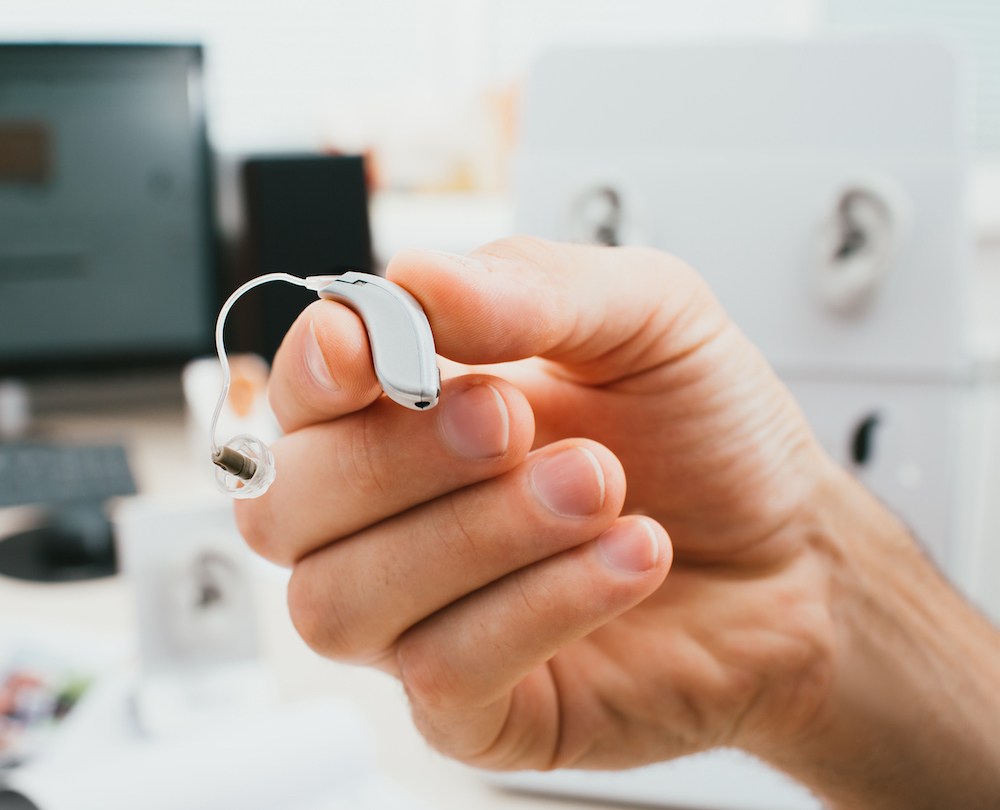

Hearing aids are a terrific solution if you are experiencing hearing loss.